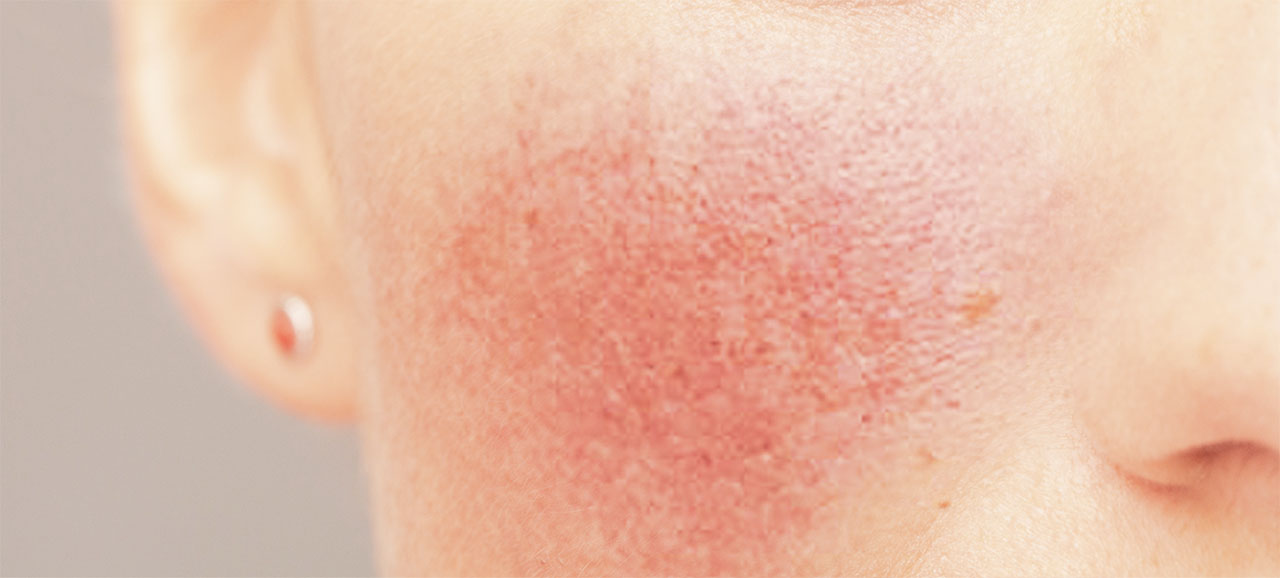
Rosacea (rosacea, acne rosacea, rosaceus, pink eels, acne pink) is a non-infectious, chronic inflammatory disease of the face skin, which is characterized by a stage of the current.
In the modern world, the prevalence of rosacea is 10% among the total population. The share of pink eels in Russia among all dermatological diagnoses is about 5%.
The disease usually begins in the 3rd-4th decade of life and reaches its peak at the age of 40-50 years.
It is more common in people of predominantly mature age, both sexes.
Causes of occurrence
The pathological process is based on changes in the tone of surface skin vessels of the face, which are caused by various internal and external factors, the action of which leads to the persistent expansion of skin vessels and subsequent blood stasis.
External factors:
- Physical factors (sun, heat, cold)
- Alimentary factors (consumption of alcohol, hot drinks, spices).
- Internal factors:
- Pathology of the digestive tract (diseases associated with H. pylori);
- Activity of Demodex ticks (brevis and folliculorum):
- The main cause of rosacea was previously thought to be the microscopic tick Demodex (Demodex folliculorum), which inhabits the sebaceous glands of hair follicles. It was supposed that the “subcutaneous tick” causes a special disease – demodex, which provokes rosacea. It is now known that demodex can also be found in perfectly healthy people. Most scientists attach a secondary importance to demodex in rosacea development. The discovery of Demodex may not be the cause, but a consequence of skin changes. The existence of a disease such as demodex has long been debated in humans, but some doctors still continue to fight the tick, believing that they are treating a specific infection and forgetting about other causes of the rash.
- Infectious skin diseases;
- Pathology of the endocrine system;
- Changes in the immune status of the body;
- Influence of blood clotting system components on vessels;
- Vascular-neurotic reactions.
Classification
There are many classifications of rosacea. Depending on the course of the disease and the intensity of formation of skin elements, the pathology may have the following stages:
- erythematous;
- papulea;
- pustulesis;
- infiltrate-productive.
Taking into account the variants of clinical picture and symptoms of rosacea, it is divided into the following forms:
- Persevering facial edema.
- Ophthalmic rosacea (in this form, eye damage in the form of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, iridocyclitis is observed).
- Granulomatous rosacea (multiple elements located around the mouth and eyes, leading to a characteristic symptomatology in the form of multiple granules).
- Steroid rosacea (formed as a result of the use of local corticosteroids for a long time, with atrophic skin and bright colored rosacea elements).
- Gram-negative rosacea (the name comes from secondary gram-negative microflora, which leads to purulent lesions of the skin and hair follicles).
- Conglobal rosacea (a severe form of disease, characterized by the formation of drain cavities and abscesses).
- Lightning-fast flow of rosacea (observed in young women, has a fast and rapid flow).
- Halogen-conditioned rosacea (activation of the process is caused by the influence of halogen-containing substances such as iodine).
- Rhinophyma and other fibrous changes in the face skin.
Clinical picture of the disease
At the beginning of the disease, redness (erythema) is observed on the skin, which has a coming character. The duration of episodes may vary from a few minutes to several hours. Appearance of erythema is provoked by various factors (being under direct sunlight, alcohol consumption, stress, physical activity, and many others). Patients feel an increase in body temperature in the affected areas. Then redness is spontaneously eliminated. Favorite places of localization are the forehead, nose, and cheeks.
Later on, pathological vascular plexuses – telangiectasia – begin to form.
In addition, there is a cystic change of lymphatic vessels. The skin acquires a stronger cyanotic shade and thickens. In the next stage, the skin forms papules, which are pink or red colored, slightly elevated above its surface, which is not undergoing any changes. Similarly, the neoplasms may spontaneously undergo reverse development.
After joining secondary infection, there is papule festering, pustules are formed. Above the surface of papules and pustules may have thickened skin scales. Some papules undergo aseptic inflammation.
There is an increase in skin glands, which begin to produce excess sebum.
The elements of rosacea can merge into extensive infiltrates, there is a rapid growth of dense fibrous tissue, which violates the true skin structure. Deformations of the face shape may occur.
Treatment
The treatment of rosacea is complex and includes the prescription of products for external and systemic use.
Patients should take care of their skin hygiene. Women should choose cosmetics that do not contain alcohol, acetone and oil and other irritants. It is better to avoid creams and ointments containing hormonal supplements, as well as exclude masks and balms with vasodilating ingredients. For washing it is necessary to use water of room temperature. Cleansing fluid should be applied by light touching your fingertips, and use a face towel with a soft cloth. Men with rosacea should use an electric shaver instead of blades.
It is necessary to protect the skin from the sun, avoid sunburns, as UV light leads to an exacerbation of the disease. In winter women should use fat cream and powder, and in heat – special products with sun filters (SPF – sun protection factor should be at least 20).
A gentle diet should also be followed, especially if rosacea is caused by functional diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to limit the consumption of spicy, salty, sour and spicy dishes, avoid alcoholic drinks, coffee, strong tea, etc. Diet correction should be done under the supervision of the attending physician.
Local treatment includes various creams, gels with azelaic acid, metronidazole, anti-inflammatory and astringent lotions, use of thermal water, and, if a tick Demodex is detected, antiparasitic drugs.
If the inflammation is depressed, antihistamines are prescribed.
It is important to use vitamins that strengthen the vascular wall (vitamin C, P (rutin)).
In severe forms and adherence to gram-negative microflora shows the use of antibiotics.
To eliminate dilated vessels in the late stages are used and methods such as electrocoagulation (exposure to weak electric current), cryodestruction (exposure to liquid nitrogen), dermabrasion and special types of lasers.
Prevention of rosacea
Prevention of the disease is to eliminate or reduce the factors contributing to it: protect the skin from tanning and hypothermia, avoid spicy dishes, alcoholic and hot drinks, use alcohol-free cosmetics, protect the skin from



